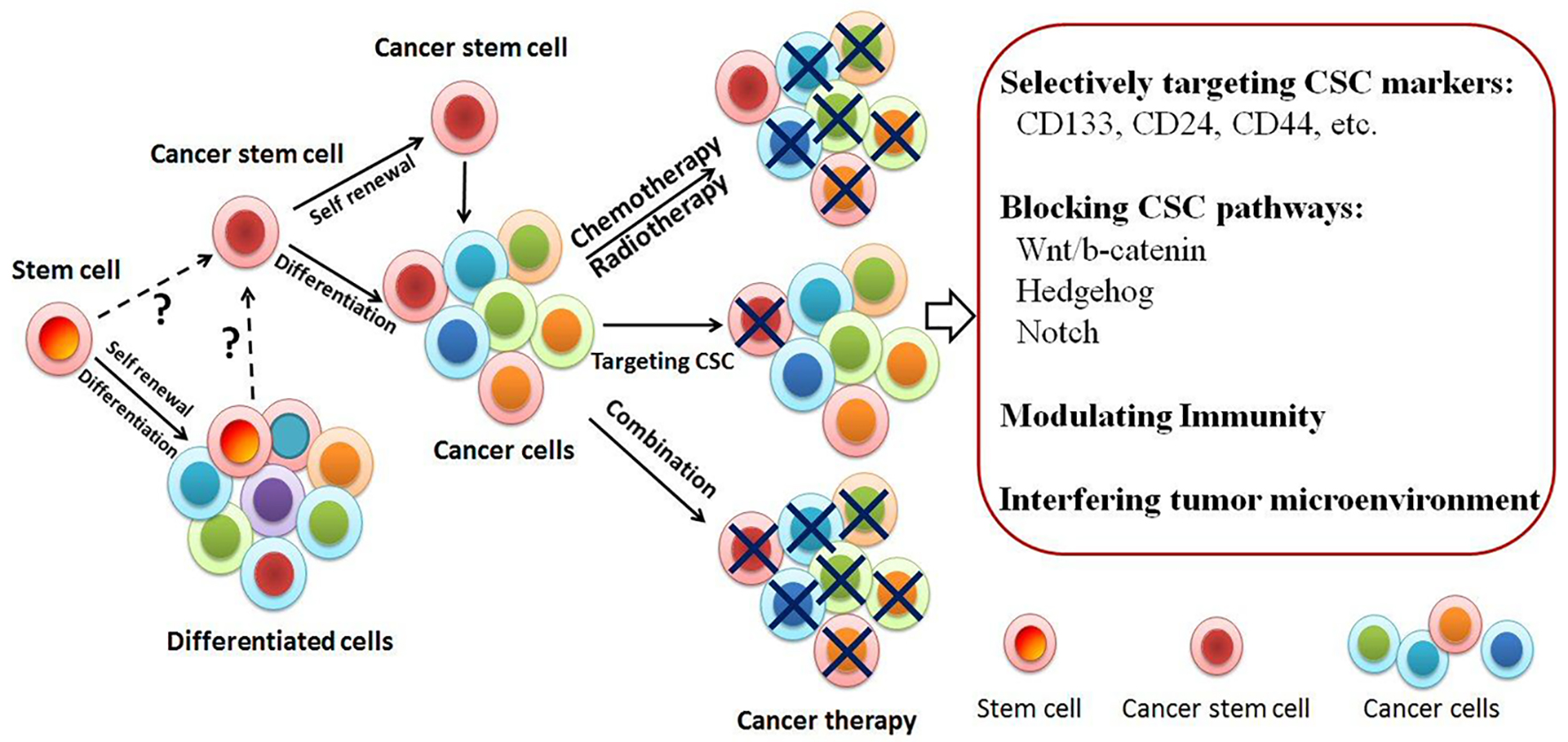
Figure 1. Tumor initiation models. Tumor-initiating cells/cancer stem cells (TICs/CSCs) may be the critical target to eradicate tumor. The origin of CSC is unknown yet. It might come from stem cells or somatic cells. CSCs known as tumorigenic cells are biologically distinct from diverse subpopulations. Cancer cell heterogeneity often leads to resistance to chemoradiation treatment. Drug-resistant cells contain CSC enrichment. Novel approaches targeting CSC have been developed either targeting the surface molecules or blocking the pathways. Selectively targeting CSC has shown promising and may open a new venue for the treatment of cancer.