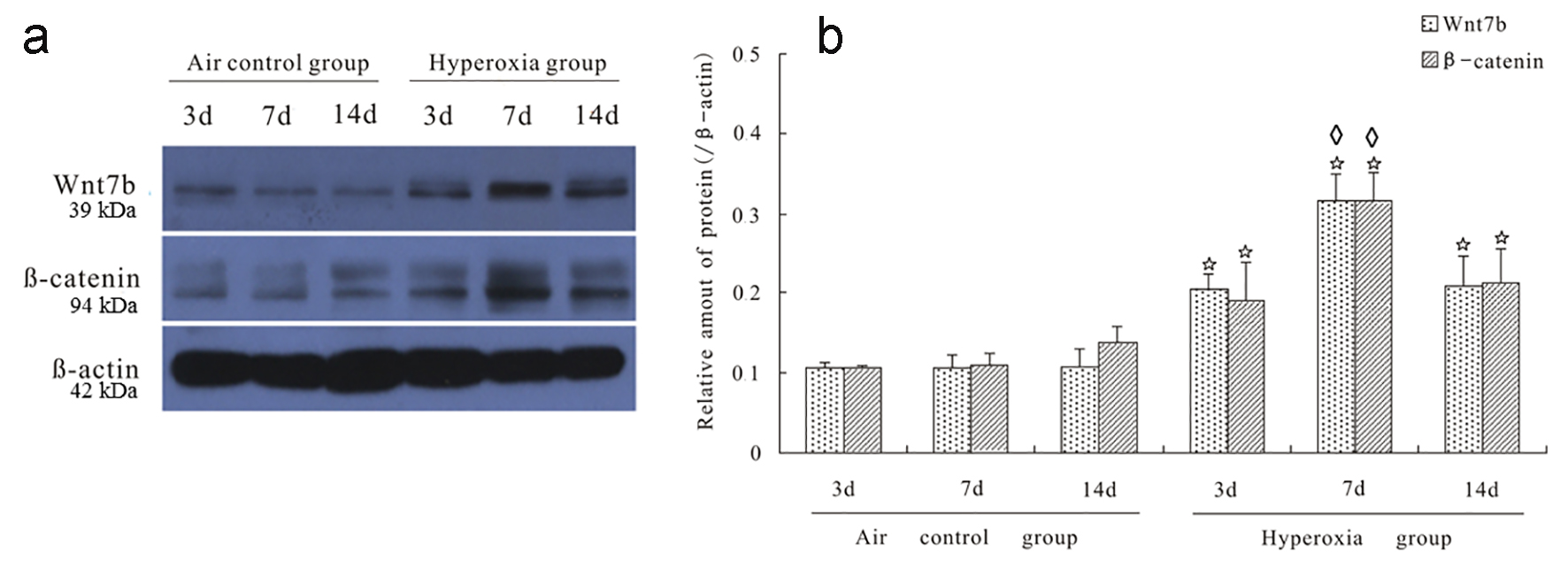
Figure 1. Hyperoxia increased the expression of Wnt7b and β-catenin proteins in rat lungs. Panel a shows a representative Western blot for Wnt7b and β-catenin protein analysis in rat lungs. Under normoxia, Wnt7b and β-catenin proteins maintained at a consistent level at all time points observed (panels a and b). In contrast, hyperoxia increased the expression of Wnt7b and β-catenin proteins in rat lungs at all time points (panels a and b). *P < 0.05 compared with their respective controls at the same time point. In the hyperoxic group, at day 7, both Wnt7b and β-catenin protein levels were significantly higher than their respective levels at other two time points (◊P < 0.05).
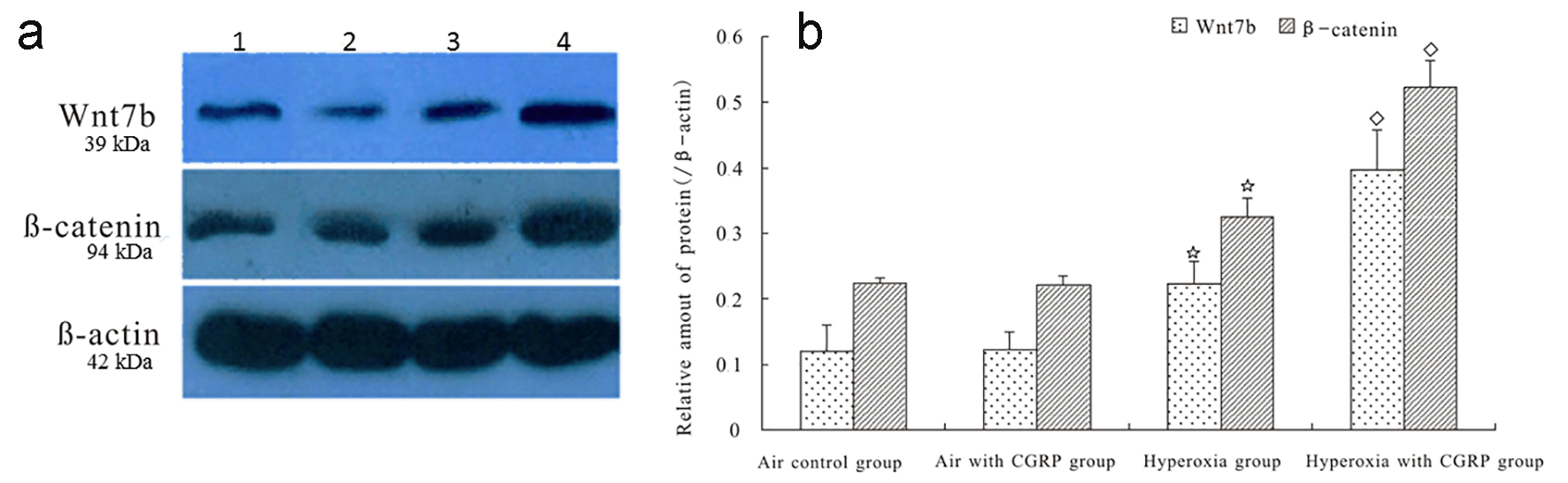
Figure 2. CGRP enhanced hyperoxia-induced expression of Wnt7b and β-catenin proteins in AEC II. There was no significant difference in Wnt7b and β-catenin protein levels between AEC II under normoxia and normoxia plus CGRP (panels a and b). However, hyperoxia induced a markedly increased expression of Wnt7b and β-catenin proteins (*P < 0.05), which was significantly enhanced by CGRP (◊P < 0.05, panels a and b). 1 = Air control; 2 = Air with CGRP; 3 = Hyperoxia; and 4 = Hyperoxia with CGRP.
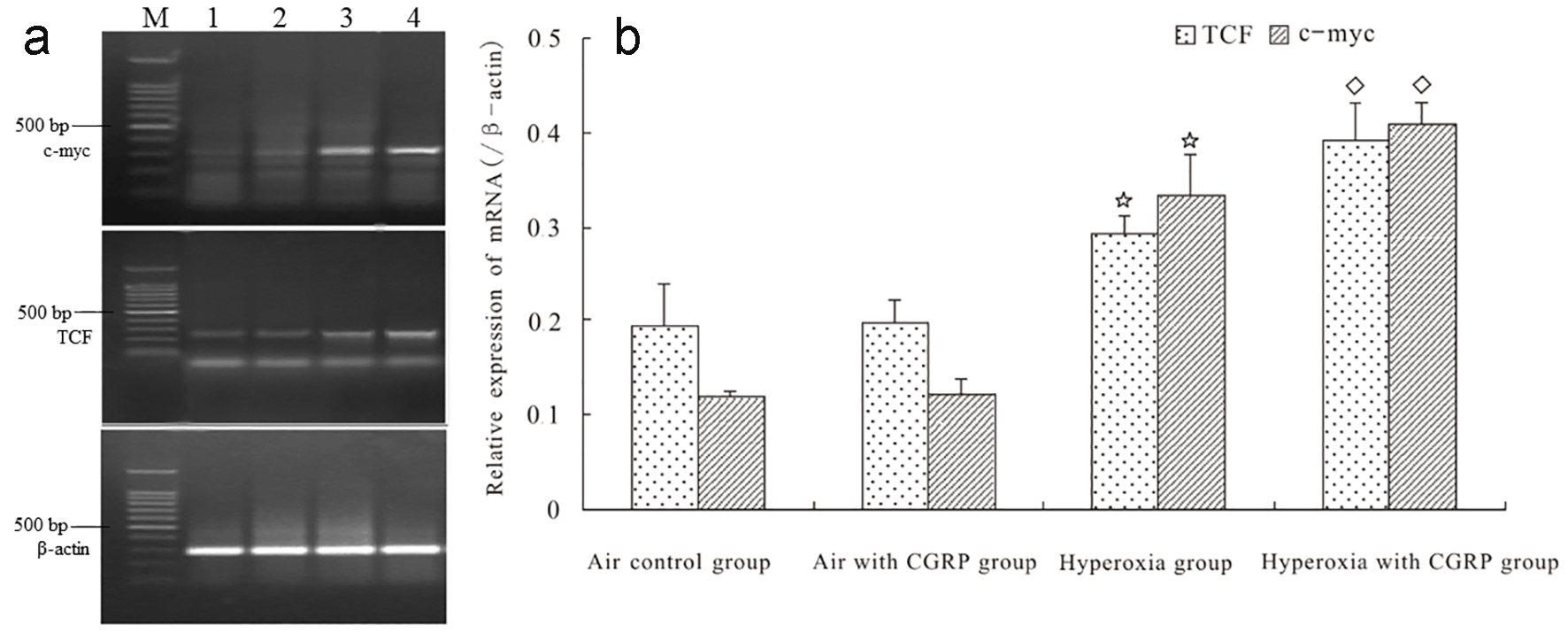
Figure 3. CGRP enhanced hyperoxia-induced mRNA expression of TCF and c-myc in AEC II. TCF and c-myc mRNA levels were similar between AEC II under normoxia and normoxia plus CGRP (panels a and b). In contrast, hyperoxia resulted in significantly elevated TCF and c-myc mRNA expression (*P < 0.05), which was further boosted by CGRP treatment (◊P < 0.05, panels a and b). M = DNA size marker; 1 = Air control; 2 = Air with CGRP; 3 = Hyperoxia; and 4 = Hyperoxia with CGRP.


